Table of Contents
| Location and Size | Credit and Collections |
| Government | Risk Assessment |
| Legal System | Business Climate |
| Interesting Facts | Business Protocol |
| Economy | Other Sources of Info |
| Comparative Economic Indicators |
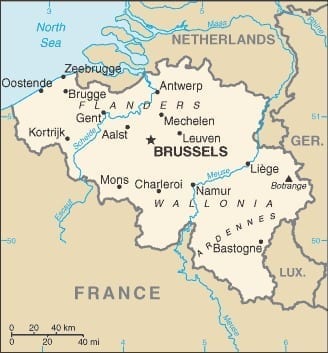
Location and Size
Belgium is located in Western Europe between France and the Netherlands, bordering the North Sea. Its land area is 30,278 sq. km, making it approximately the size of Maryland.
Government
A federal parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy. Belgium has 3 regions: French, Dutch and Brussels Capital. As a result of the 1993 constitutional revision that furthered devolution into a federal state, the country now has three levels of government: federal, regional, and linguistic community.
Branches of the Belgian Government:
Executive:
- Chief of State: King PHILIPPE (Heir Apparent: Princess ELISABETH, daughter of the monarch)
- Head of Government: Prime Minister Alexander DE CROO
- Cabinet: Council of Ministers formally appointed by the monarch
Legislative: bicameral Parliament consisting of:
- Senate (60 seats; 50 members indirectly elected by popular vote, 10 elected by 50 other senators)
- Chamber of Representatives (150 members directly elected by popular vote; members serve 5-year term)
Judicial:
- Constitutional Court (12 judges appointed by the King; 6 Dutch-speaking and 6 French-speaking)
- Supreme Court of Justice (judges appointed for life by the government)
Legal System
Belgium has a civil law system based on the French Civil Code. Its law continues to be modified in conformance with the legislative norms mandated by the European Union.
Belgium accepts compulsory International Court of Justice (ICJ) jurisdiction with reservations. Belgium also accepts ICCt jurisdiction.
Interesting Facts About Belgium
- More than 800 kinds of beer are made in Belgium; Belgians consume an average 150 liters of beer per person per year
- Belgium produces 220,000 tons of chocolate per year
- Belgium has one of the lowest proportion of McDonald’s restaurants in the developed world: just 0.062 per inhabitant, which is 1/7 the U.S. proportion, 1/4 that of Japan, and 1/2 of France and Germany
- Belgium legalized euthanasia in 2002 and gay marriage in 2003
- Belgium requires its citizens to vote, and enforces the requirement
- The Belgian motorway system is the only man-made structure visible from the moon
- Belgium produces the greatest variety of bricks in the world
- Brussels is home of the world’s deepest swimming pool: 35 meters deep
Economy
Belgium is a relatively prosperous country. However, with few natural resources, Belgium must import substantial quantities of raw materials in order to export a large volume of manufactures. This makes its economy vulnerable to volatility in world markets.
Roughly three-quarters of Belgium’s trade is with other EU countries. Belgian banks were severely affected by the international financial crisis with three major banks receiving capital injections from the government. An aging population and rising social expenditures are also mid- to long-term challenges to public finances.
Belgium’s GDP grew by 1.7% in 2017 and the budget deficit was 1.5% of GDP. Former Prime Minister Charles MICHEL’s center-right government had pledged to further reduce the deficit in response to EU pressure to decrease Belgium’s high public debt of about 104% of GDP, but such efforts had also dampened economic growth. In addition to restrained public spending, low wage growth and higher inflation promise to curtail a more robust recovery in private consumption.
The government has pledged to pursue a reform program to improve Belgium’s competitiveness, including changes to labor market rules and welfare benefits. These changes have generally made Belgian wages more competitive regionally, but have raised tensions with trade unions, which have called for extended strikes.
Leading Markets (2021): Germany 17%, France 14%, Netherlands 13%, UK 8%, US 6%, Italy 5%
Leading Exports – Commodities: Cars and vehicle parts, refined petroleum, packaged medicines, medical cultures/vaccines, diamonds, natural gas
Leading Suppliers (2021): Netherlands 16%, Germany 13%, France 10%, US 8%, Ireland 5%, China 5%
Leading Imports – Commodities: Cars, refined petroleum, packaged medicines, medical cultures/vaccines, diamonds, natural gas
Top Industries: Engineering and metal products, motor vehicle assembly, transportation equipment, scientific instruments, processed food and beverages, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, base metals, textiles, glass, petroleum
Top Agricultural Products: Sugar beet, milk, potatoes, wheat, pork, lettuce, poultry, maize, barley, pears
Comparative Economic Indicators – 2021
| Belgium | France | Netherlands | Luxembourg | Germany | USA | |
| Population (millions) | 11.77 | 68.08 | 17.34 | 0.639 | 79.90 | 334.99 |
| Population growth rate (%) | 0.59 | 0.33 | 0.37 | 1.7 | -0.21 | 0.7 |
| Age Structure (%) (15 to 64 years old) | 63.57 | 61.18 | 64.07 | 67.90 | 64.13 | 64.69 |
| Age Structure (%) (65+ years old) | 19.21 | 20.46 | 19.82 | 15.37 | 22.99 | 16.85 |
| Literacy (%) | 99.0 | 99.0 | 99.0 | 99.0 | 99.0 | 99.0 |
| Unemployment (%)* | 5.36 | 8.12 | 3.41 | 5.36 | 4.98 | 3.89 |
| Inflation (%)* | 1.14 | 1.1 | 2.6 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1.8 |
| Population below poverty line (%) | 14.8 | 13.6 | 13.6 | 17.5 | 14.8 | 15.1 |
| GDP** (USD billions) | 533.0 | 2,715.6 | 986.8 | 71.1 | 4,482.4 | 21,524.9 |
| GDP real growth rate** (%) | 1.4 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 0.59 | 2.16 |
| GDP per capita** (USD) | 51,934 | 46,184 | 56,935 | 71,089 | 53,919 | 62,530 |
| Public debt (% of GDP) | 103.4 | 96.8 | 56.5 | 23.0 | 63.9 | 78.8 |
| Exports (USD billions) | 474.3 | 969.1 | 857.6 | 133.6 | 2,004.1 | 2,377.1 |
| Imports (USD billions) | 473.1 | 1,021.6 | 755.6 | 111.3 | 1,804.4 | 3,214.2 |
| Currency | Euro EUR |
Euro EUR |
Euro EUR |
Euro EUR |
Euro EUR |
Dollar
USD
|
| Exchange rates (per USD) 05/25/2021 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 1.22 | n/a |
| Exchange rates (per EUR) 05/25/2021 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0.82 |
* May 2021 estimates
Economic Data from CIA World Factbook
Credit and Collections
Collecting in Belgium is rather normal. There are no laws or other impediments to collecting.
The following information on debt collection in Belgium was provided to us by Eric Van Even, Credit Control Manager, Gosselin Group NV, Belgium.
Belgium law states that, if no payment term has been agreed upon, interest is due automatically 30 days following the date the customer receives the invoice or an equivalent payment request. If this date is uncertain, interest becomes due after the receipt of goods/services or 30 days after the date on which acceptance or verification takes place. The applicable interest rate is fixed at the European Central Bank. The creditor is also entitled to claim reasonable compensation for recovery costs.
Every business established in Belgium is required to file a certified copy of its annual accounts and balance sheet with the National Bank of Belgium. This information is public and copies can be obtained on demand.
Legal Protections
Attachment: If the delinquent customer posses real estate or personal property, it is possible to seize these goods for security. The customer will continue to have title of ownership; he cannot sell the attached goods or further organize his own insolvency. However, the debt must fulfill the following conditions:
- It must be certain. An attachment will not be allowed for potential, conditional or disputed debts.
- It must be payable. The debt is past due.
- It must be fixed. The amount of the debt must be specified or can easily be specified.
Law Suit: Normally, legal action commences by serving a writ on the customer. This writ must include:
- The identity of the parties.
- The subject of the claim and a short summary of the grounds on which the claim is based.
- The judges by whom the case will be heard.
- The time and place of the first court hearing.
Arbitration. Belgium signed the U.N. 1958 Convention on the Recognition and Enforcement of Foreign Arbitral Awards in 1958. This Convention was ratified in Belgium on August 18, 1975.
Risk Assessment
Coface Country Rating: A3 – Low risk
Coface Business Climate Rating: A1 – Low risk
According to Coface, Belgium will make a return to growth in 2021, after being one of the countries hardest hit by the pandemic in 2020, both in terms of health (highest number of deaths per inhabitant at the end of 2020) and the economy. As the health situation gradually improves, domestic demand is expected to rebound sharply in 2021.
Credendo Political Risk Rating: 1 – Lowest risk
Credendo Commercial Risk Rating: E – Moderate risk
Business Climate
This modern, open, and private-enterprise-based economy has capitalized on its central geographic location, highly developed transport network, and diversified industrial and commercial base.
With exports and imports approximately equal to GDP, Belgium depends heavily on world trade. Belgium’s trade advantages are derived from its central geographic location and a highly skilled, multilingual, and productive work force.
Most of Belgium’s trade is with fellow EU member states. As a result, Belgium seeks to diversify and expand trade opportunities with non-EU countries.
Economic Freedom: According to The Heritage Foundation’s 2021 Index of Economic Freedom, Belgium’s score is 70.1, making it the 37th freest economy in the 2021 Index. Belgium is ranked 22nd freest among the 45 countries in the European region and its overall score is equal to the regional average but above the global averages.
Regulatory System: Complex sharing of authority between regions, linguistic communities, and the federal government make the regulatory system difficult to navigate.
Corruption: Per Transparency International’s 2020 Corruption Perceptions Index, Belgium received a score of 7.6 out of 10 (fairly free of corruption). It ranked 15th out of 180 countries rated.
For more detailed information on these topics, visit the 2020 Investment Climate Statement – Belgium of the U.S. Department of State.
Business Protocol in Belgium
- Belgians take time to trust others.
- They often engage in long, critical discussions before reaching a decision so that they can be certain that they have considered all the alternatives.
- Business dealings tend to be bureaucratic. There are many procedures and a great deal of paperwork.
- Belgians are excellent linguists and many are sufficiently fluent to conduct meetings in English.
- Belgians prefer subtlety to directness, believing that subtlety is a reflection of intelligence.
- Although it is becoming increasingly common for colleagues to use first names at work, this practice remains rare when there is a distinct difference in age or position and when dealing with ‘outsiders’ such as clients or suppliers.
- Women remain in a largely subordinate position to men in business, but this situation is changing and female business travelers usually find acceptance throughout corporate Belgium, especially in the major cities.
Sources for further information on doing business in Belgium
Doing Business guide in Belgium, PricewaterhouseCoopers
Embassy of the United States, Brussels, Belgium
**********
Subscribe to the Credit-to-Cash Advisor
Monthly e-Newsletter — It’s Free
This information is provided by ABC-Amega Inc. Providing international receivable management and debt collection services for exporters to more than 200 countries including Belgium. For further information, contact [email protected].
This report represents a compilation of information from a wide variety of reputable sources.
Comparative Economic Indicators: CIA World Factbook
Exchange Rates: OANDA.com The Currency Site.